
Related Topics
About AP Client Isolation
When you configure an SSID for your AP, you can optionally enable client isolation. The client isolation setting enables you to control whether wireless clients can communicate directly to each other through an AP. Client isolation prevents direct traffic between wireless clients that connect to the same SSID on the same radio.
You can also use client isolation to prevent traffic between wireless clients that use the same SSID on different APs, but this requires additional configuration with VLANs as described in the following sections.
We recommend that you enable client isolation for SSIDs on APs that provide a wireless guest network for wireless clients that do not trust each other.
Client Isolation for a Single AP
To enable client isolation on an AP, select the Enable client isolation check box in the SSID settings.
For more information, see Configure WatchGuard AP SSIDs.
Client Isolation for Multiple APs
When client isolation is enabled on a single AP that uses the same SSID as another AP, traffic can still pass between wireless clients that are connected to other APs. To effectively implement client isolation for an SSID that is used by more than one AP, you must also make sure that all traffic between your APs goes through the Firebox. The Firebox can then use VLANs to apply policies that support your client isolation settings to the traffic.
You can use a VLAN with client isolation to prevent direct traffic between wireless clients that use the same SSID while connected to different APs.
To implement client isolation for more than one AP, you must:
- Add a VLAN and configure it to apply firewall policies to intra-VLAN traffic.
To make sure that the same IP address pool is used for wireless clients that connect to the SSID on any AP, you must configure a VLAN. For wireless roaming to function correctly, all SSIDs must be on the same network. When you configure the VLAN to apply policies to intra-VLAN traffic, the Firebox applies firewall policies to the VLAN traffic from one interface with the destination of the same VLAN on another interface.
- For each AP, configure one VLAN interface to manage untagged VLAN traffic.
Or, enable communication VLAN tagging in the AP configuration and select a VLAN ID to use for management communications.
- Configure the SSID settings to enable client isolation.
It is not necessary to enable VLAN tagging in the SSID settings if the VLAN interfaces are configured to manage untagged traffic.
- Connect each AP directly to a VLAN interface on the Firebox.
This ensures that all traffic between APs goes through the Firebox.
Because the default firewall policies automatically deny traffic between APs on two different interfaces, you do not have to create a policy to explicitly deny that traffic. For example, if you configure a VLAN in the Optional security zone, the Firebox automatically denies packets between the two interfaces as unhandled packets because they do not match any of the configured firewall policies. To prevent traffic between APs, make sure that you do not add a policy that allows traffic from Optional to Optional.
You can also enable VLAN tagging in the SSID and configure the VLAN interfaces to manage tagged traffic, but VLAN tagging is not required for client isolation. If you enable VLAN tagging, you must configure two VLANs: one for tagged SSID traffic and one for untagged management communications traffic. Or, you can enable one VLAN and configure the AP to enable management communications VLAN tagging for that VLAN in the AP configuration.
For more information, see Configure VLANs for WatchGuard APs.
Example — Client Isolation and Roaming
This example shows how to implement client isolation for a wireless guest network with two AP100 devices that use the same SSID.
Step 1 — Configure the VLAN
First, configure the VLAN interfaces and VLANs for your APs.
- Configure two Firebox interfaces as VLAN interfaces.
For example, the two VLAN interfaces could have these settings:- Interface Names — AP100-1 and AP100-2
- Interface Type — VLAN
- Create a VLAN to use for traffic to an SSID.
For example, the VLAN could have these settings:- Name — AP100-Guest
- VLAN ID — 20
- Security Zone — Optional
- IP Address — 10.0.20.1/24
- VLAN tag settings — Untagged traffic for VLAN interfaces AP100-1 and AP100-2
- Apply firewall policies to intra-VLAN traffic — Enabled
- Network — DHCP Server Address Pool: 10.0.20.10 to 10.0.20.100

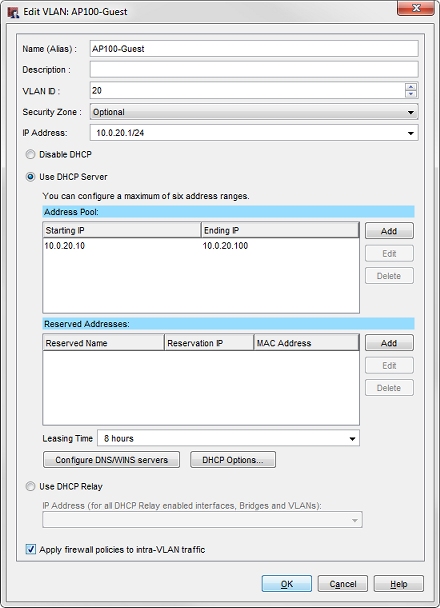
- Create a VLAN to apply VLAN tagging to traffic to an SSID.
For example, the VLAN could have these properties:- Name (Alias) — AP100-Guest
- VLAN ID — 20
- Security Zone — Optional
- IP Address — 10.0.20.1/24
- DHCP Server Address Pool — 10.0.20.10 to 10.0.20.100
- Apply firewall policies to intra-VLAN traffic — Enabled
- Configure a VLAN interface on the first AP.
For example, the first VLAN interface could have these properties:- Interface Name — AP100-1
- Interface Type — VLAN
- Send and received untagged traffic for VLAN AP100-Guest (10.0.20.1/24)

- Configure a VLAN interface on the second AP.
For example, the second VLAN interface could have these properties:- Interface Name — AP100-2
- Interface Type — VLAN
- Send and received untagged traffic for VLAN AP100-Guest (10.0.20.1/24)
For more information about how to configure a VLAN, see Define a New VLAN.
Step 2 — Configure the SSID
Next, enable client isolation in the SSID settings.
- Add or edit an SSID for your wireless guest network.
- Select the Enable client isolation check box.

Because the AP-Guest VLAN in this example is an untagged VLAN, you do not have to enable VLAN tagging in the SSID settings.
- Add or edit an SSID for your wireless guest network.
- Select the Enable client isolation check box.

Because the AP-Guest VLAN in this example is an untagged VLAN, you do not have to enable VLAN tagging in the SSID settings.
For more information about SSID configuration, see Configure WatchGuard AP SSIDs.
Step 3 — Connect the APs to the VLAN Interfaces
After you configure the VLAN interfaces and SSID settings:
- Connect the APs to the VLAN interfaces.
- Discover and pair each AP.
- Configure both APs to use the SSID you configured.
For more information about discovery and pairing, see WatchGuard AP Discovery and Pairing.
About This Example
This configuration example prevents direct wireless traffic between wireless clients that connect to the AP100-Guest SSID. The two main components of this configuration are:
- Client isolation — The client isolation setting in the SSID makes sure that wireless clients that connect to the same radio from cannot connect directly to each other.
- VLAN — The firewall and VLAN configuration make sure that traffic cannot pass between wireless clients that connect to the AP100-Guest SSID on different APs.
This example shows how to configure client isolation for two APs. To add a third AP, configure another VLAN interface to handle untagged VLAN traffic for the defined VLAN. Then, connect the AP to that VLAN interface and configure it to use the defined SSID.