
Related Topics
Enable Wireless Connections
You can enable Access Point 1, Access Point 2, or Access Point 3 on your wireless Firebox for any network type, and configure the wireless interfaces with the same type of settings as an internal network interface.
The wireless interfaces appear on the network Interfaces page with these default interface names:
| Access Point | Interface Name |
|---|---|
| Access Point 1 | ath1 |
| Access Point 2 | ath2 |
| Access Point 3 | ath3 |
For more information about network interfaces, see About Network Modes and Interfaces.
- Select Network > Wireless.
The Wireless configuration page appears.

- Select the Enable wireless check box.
- Select Enable wireless access points.
- Adjacent to Access point 1 or Access point 2, or Access point 3, click Configure.
The Wireless Access Point configuration dialog box appears.

- In the Interface Name (Alias) text box, you can change the alias name of the interface or use the default name.
- From the Interface Type drop-down list, select an interface type for this Access Point interface.
- Trusted
- Optional
- Bridge
- VLAN
- Custom
If you want your wireless users to be on the same network as your wired trusted or optional network, you must use a network bridge between the wireless interface and the trusted or optional wired interface. For more information, see Create a Network Bridge Configuration.
For detailed instructions on how to bridge a wireless interface to the trusted interface, see the Bridge a Firebox wireless interface to the trusted interface article in WatchGuard Knowledge Base.
- Click OK.
- Select the Wireless tab.

- To configure the wireless interface to send and answer SSID requests, select the Broadcast SSID check box.
- To send a log message each time a wireless computer tries to connect to the interface, select the Log Authentication Events check box.
- To allow wireless guest users to send traffic to each other, clear the Prohibit client to client wireless network traffic check box.
- To require wireless users to use the WatchGuard Mobile VPN with IPSec Client, select the Require encrypted Mobile VPN with IPSec connections for wireless clients check box.
When you select this option, the Firebox only allows the DHCP, DNS, IKE (UDP port 500), and ESP packets over the wireless network. If you require wireless users to use the IPSec Mobile VPN Client, it can increase the security for wireless clients if you do not select WPA or WPA2 as the wireless authentication method.
- In the Network name (SSID) text box, type a unique name for your wireless optional network, or use the default name.
- From the Encryption (Authentication) drop-down list, select the encryption and authentication setting to enable for wireless connections to the optional interface.
WatchGuard recommends the default setting of WPA2 Only. - From the Encryption algorithm drop-down list, select the type of encryption to use for the wireless connection and specify the keys or passwords required for the type of encryption you select.
If you select an encryption option with pre-shared keys, a random pre-shared key is generated for you. You can use this key or type another key. - Save the configuration.
- Select Network > Wireless.
The Wireless Configuration dialog box appears.
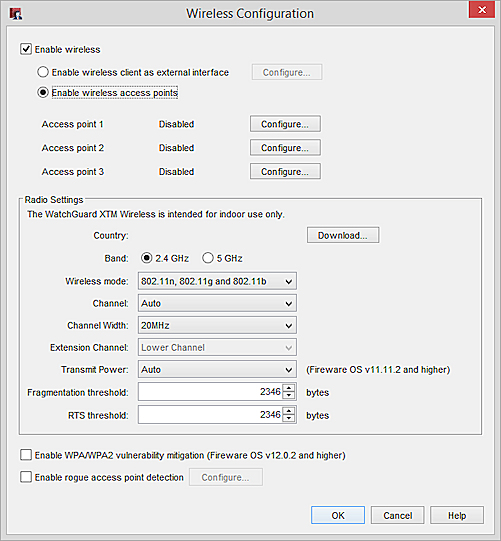
- Select the Enable wireless check box.
- Select Enable wireless access points.
- Adjacent to Access point 1 or Access point 2, or Access point 3, click Configure.
The Wireless Access Point configuration dialog box appears.

- In the Interface Name (Alias) text box, you can change the alias name of the interface or use the default name.
- From the Interface Type drop-down list, select an interface type for this Access Point interface.
- Trusted
- Optional
- Bridge
- VLAN
- Custom
If you want your wireless users to be on the same network as your wired trusted or optional network, you must use a network bridge between the wireless interface and the trusted or optional wired interface. For more information, see Create a Network Bridge Configuration.
For detailed instructions on how to bridge a wireless interface to the trusted interface, see the Bridge a Firebox wireless interface to the trusted interface article in the knowledge base.
- Click OK.
- Select the Wireless tab.

- To configure the wireless interface to send and answer SSID requests, select the Broadcast SSID check box.
- To send a log message each time a wireless computer tries to connect to the interface, select the Log Authentication Events check box.
- To allow wireless guest users to send traffic to each other, clear the Prohibit client to client wireless network traffic check box.
- To require wireless users to use the WatchGuard Mobile VPN with IPSec Client, select the Require encrypted Mobile VPN with IPSec connections for wireless clients check box.
When you select this option, the Firebox only allows the DHCP, DNS, IKE (UDP port 500), and ESP packets over the wireless network. If you require wireless users to use the IPSec Mobile VPN Client, it can increase the security for wireless clients if you do not select WPA or WPA2 as the wireless authentication method.
- In the Network name (SSID) text box, type a unique name for your wireless optional network, or use the default name.
- From the Encryption (Authentication) drop-down list, select the encryption and authentication to enable for wireless connections to the optional interface.
WatchGuard recommends the default setting of WPA2 Only. - From the Encryption algorithm drop-down list, select the type of encryption to use for the wireless connection and specify the keys or passwords required for the type of encryption you select.
If you select an encryption option with pre-shared keys, a random pre-shared key is generated for you. You can use this key or type another key. - Save the configuration.
If you enable wireless connections to the trusted interface, we recommend that you restrict access by MAC address. This is to make it more difficult for users to connect to the wireless Firebox from unauthorized computers.
To enable MAC access control:
- Select the MAC Access Control tab.
- Configure the settings to restrict network traffic on an interface, as described in Restrict Network Traffic by MAC Address.
Wireless and wired networks operate as if they are on the same local network. Broadcast traffic, such as DHCP requests, can pass between wired and wireless clients. If a DHCP server is active on the physical network, or if a wireless client is configured as a DHCP server, then all wired and wireless clients on that network can receive IP addresses from that DHCP server.
See Also
Wireless Device Configuration Options
About Network Modes and Interfaces
Enable or Disable SSID Broadcasts
Change the Fragmentation Threshold