Applies To: WatchGuard Advanced EPDR, WatchGuard EPDR, WatchGuard EDR, WatchGuard EPP
The Exploit Activity table shows the exploit technique detected, as well as the name of the compromised program.
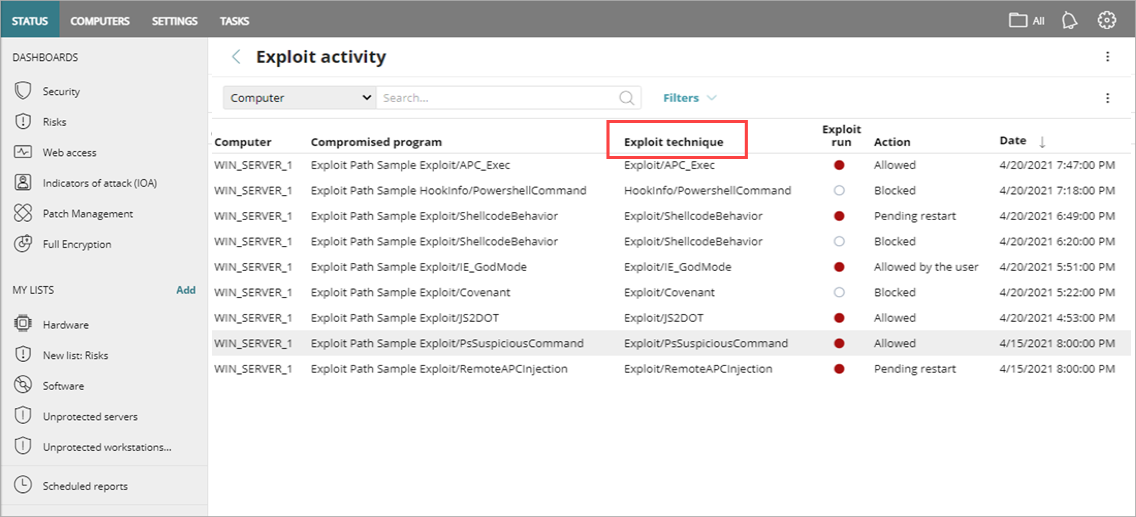
These are the different techniques monitored:
Exploit/Metasploit
The Metasploit Framework is a testing platform that enables its users to create, test, and execute exploit code. If Endpoint Security detects a metasploit shellcode signature, it appears as an Exploit/Metasploit exploit technique.
Exploit/ReflectiveLoader
Reflective DLL injection uses reflective programming to load a library from memory into a host process without detection. If Endpoint Security detects a reflective executable loading (for example, metasploit or cobalt strike), it appears as an Exploit/ReflectiveLoader exploit technique.
Exploit/RemoteAPCInjection
The asynchronous procedure call (APC) is a legitimate way to run code in a process thread that waits for data without consuming resources. To evade process-based defenses and possibly elevate privileges, attackers can use the APC queue to inject malicious code into a process. APC injection executes arbitrary code in the address space of a separate live process. If Endpoint Security detects remote code injection by an APC, it appears as an Exploit/RemoteAPCInjection exploit technique.
Exploit/DynamicExec
Code injections occur when applications allow the dynamic execution of code instructions from untrusted data. An attacker can influence the behavior of the targeted application and modify it to get access to sensitive data. If Endpoint Security detects the execution of code in pages without execution permissions (32-bits only), it appears as an Exploit/DynamicExec exploit technique.
Exploit/HookBypass
Hooking refers to the interception of function calls, system events, or messages. The code snippets that perform these interceptions are called hooks. Endpoint Security products use hooks to monitor events in the operating system. If Endpoint Security detects a hook bypass in a running function, it appears as an Exploit/HookBypass exploit technique.
Exploit/ShellcodeBehavior
Shellcode is a small piece of machine code used as the payload in the exploitation of a software vulnerability. Exploits commonly inject a shellcode into the target process before or at the same time as they exploit a vulnerability. If WatchGuard Endpoint Security detects the execution of code on MEM_PRIVATE pages that does not correspond to a Portable Executable (PE), it appears as a ShellcodeBehavior exploit technique.
Exploit/ROP1
Return-oriented programming (ROP) is an exploit technique that enables attackers to control the call stack and program control flow. The attacker then executes machine instruction sequences that are already present in the machine memory. These instructions usually end in a return instruction and are located in a subroutine within an existing program or shared library code. If Endpoint Security detects the execution of memory management APIs when the stack is out of the thread limits, it appears as an Exploit/ROP1 exploit technique.
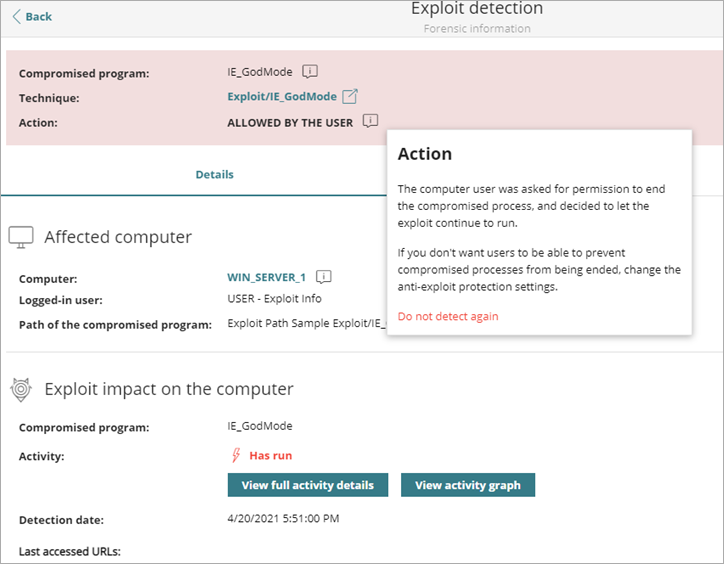
Exploit/IE_GodMode
Windows God Mode enables you to quickly access administrative tools, backup and restore options, and other important management settings from a single window. This includes Internet options. If Endpoint Security detects God Mode in Internet Explorer, it appears as an Exploit/IE_GodMode exploit technique.
Exploit/RunPE
RunPE is a type of malware that hides code inside a legitimate process. It is sometimes referred to as a hollowing technique. If WatchGuard Endpoint Security detects process hollowing techniques or RunPE, it appears as an Exploit/RunPE exploit technique.
Exploit/PsReflectiveLoader1
Hackers commonly use reflective loaders to extract sensitive information, such as passwords and credentials, from system memory. If Endpoint Security detects a PowerShell reflective loader in the computer, such as mimikatz, it appears as an Exploit/PsReflectiveLoader1.
Exploit/PsReflectiveLoader2
Hackers commonly use reflective loaders to extract sensitive information, such as passwords and credentials, from system memory. If Endpoint Security detects a PowerShell reflective loader in a remote computer (not the local computer), such as mimikatz, it appears as an Exploit/PsReflectiveLoader2.
Exploit/NetReflectiveLoader
Hackers commonly use reflective loaders to extract sensitive information, such as passwords and credentials, from system memory. If Endpoint Security detects a NET reflective loader, such as Assembly.Load, it appears as an Exploit/NetReflectiveLoader exploit technique.
Exploit/JS2DOT
js2-mode is a JavaScript editing mode for GNU Emacs (a free, customizable text editor). If Endpoint Security detects a JS2DOT technique, it appears as an exploit tech ique.
Exploit/Covenant
Covenant is a .NET collaborative command and control platform for cybersecurity professionals. If WatchGuard Endpoint Security detects the Covenant framework, it appears as an exploit technique.
Exploit/DumpLsass
Adversaries can attempt to connect to credential material stored in the process memory of the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS). If Endpoint Security detects an LSASS process memory dump, it appears as an exploit technique.
Exploit/APC_Exec
To evade process-based defenses or elevate privileges, attackers can try to inject malicious code into processes in the asynchronous procedure call (APC) queue. APC injection is a method that executes arbitrary code in a separate live process. If Endpoint Security detects local code execution through APC, it appears as an Exploit/APC_Exec exploit technique.
Vulnerable Driver
Vulnerable drivers are drivers with vulnerabilities that have been exploited in the threat landscape. This can include outdated drivers that contain security gaps.
Drivers supplied by legitimate vendors might contain vulnerabilities that malware could exploit to infect a computer or disable the security software. These drivers are not malicious in themselves and could be installed on computers without posing a security threat. Therefore, they are not initially detected as malware. Anti-exploit protection blocks the use of vulnerable drivers, except when the driver loads at operating system startup.
Exclusions
To exclude the detection of a technique for a specific program:
- On the Exploit Detection page, in the Action section, select Do not detect again for a specific program.