Applies To: Cloud-managed Fireboxes
Wireless radio settings are applied globally to the wireless networks you configure on the Firebox. For more information on how to add and configure a wireless network, see Configure Firebox Wireless.
Due to regulatory requirements in different parts of the world, some wireless radio settings are not available in every country. The country of operation is determined based on the public IP address of the wireless Firebox when you register the device with WatchGuard Cloud. WatchGuard Cloud monitors the wireless Firebox each time it connects and automatically detects if the country of operation has changed based on the public IP address of the device.
To configure wireless radio settings, from WatchGuard Cloud:
- Select Configure > Devices.
- Select the cloud-managed Firebox.
- Click Device Configuration.
- Click the Networks tile.
The Networks configuration page opens. - Go to the Wireless Settings section.
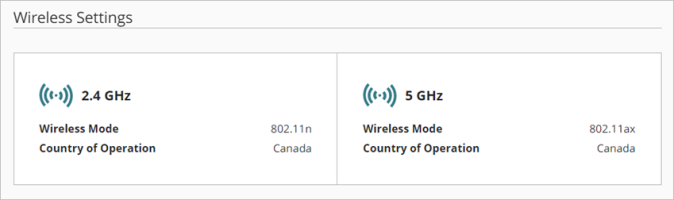
Firebox wireless models with a single dual band radio can operate on the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band. Firebox wireless models with dual radios can operate on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band.
- Click Radios Settings, or the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio depending on your Firebox model.
The Wireless Settings page opens.

Wireless Settings for Firebox with a Single Radio (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz)
Wireless Settings for Firebox with Two Radios (5 GHz radio shown)
You can configure these settings:
Frequency Band
Wireless Fireboxes have either a single radio that can operate on the 2.4 GHz band or the 5 GHz band, or dual radios that can operate on both the 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band.
- 2.4 GHz has a much better range than a 5 GHz wireless network because it uses longer wavelengths. However, the 2.4 GHz band is very congested with a lot of interference and few non-overlapping channels from which to select (1, 6, 11).
- The 5 GHz band supports faster data rates at shorter distances than the 2.4 GHz band, but has more non-overlapping channels available to reduce interference.
Wireless Mode
The frequency band you select and the regional location of the Firebox determine the wireless modes and channels available.
Dual Radio Firebox Models
The 2.4 GHz band supports these wireless modes:
- 802.11ax — This mode enables wireless devices that use 802.11b/g/n/ax to connect to the Firebox.
- 802.11n — This mode enables wireless devices that use 802.11b/g/n to connect with the Firebox.
The 5 GHz band supports these wireless modes:
- 802.11ax — This mode enables wireless devices that use 802.11a/n/ac/ax to connect to the Firebox.
- 802.11ac — This mode enables devices that use 802.11a/n/ac to connect to the Firebox.
Single Radio Firebox Models
The 2.4 GHz band supports these wireless modes:
- 802.11b/g/n — This is the default mode for Firebox wireless models with a single radio. This mode enables wireless devices that use 802.11b/g/n to connect with the Firebox.
- 802.11b/g — This mode enables wireless devices that use 802.11b/g to connect with the Firebox.
- 802.11g/n — This mode enables wireless devices that use 802.11g/n to connect with the Firebox.
- 802.11b — This mode enables wireless devices that use 802.11b only to connect with the Firebox.
The 5 GHz band supports these wireless modes:
- 802.11a/n — This is the default mode for Firebox wireless models with a single radio. This mode enables devices that use 802.11a or 802.11n to connect to the Firebox.
- 802.11n and 802.11ac — This mode enables devices that use 802.11n and 802.11ac to connect to the Firebox.
- 802.11a — This mode enables devices that use 802.11a only to connect to the Firebox.
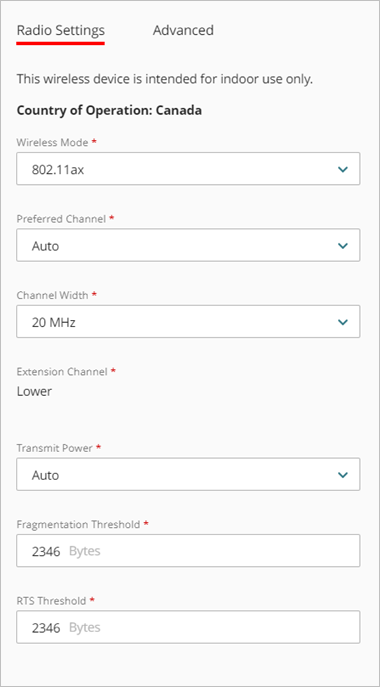
Preferred Channel
The available channels depend on the country and the wireless mode you select. By default, the preferred channel is set to Auto. In this mode, the wireless Firebox automatically selects a quiet channel from the available list of channels in the band you select.
You can also select a specific channel from the drop-down list. Make sure that you select a channel that is not already in use by another access point in your airspace.
Channel Width
Channel width controls how broad the signal is and how many frequencies the signal uses. Greater channel widths provide faster speed and throughput, but can cause greater interference in high density areas.
- The 2.4 GHz band supports 20 and 40 MHz channel widths.
- The 5 GHz band supports 20, 40, and 80 MHz channel widths.
We recommend you start with 20 to 40 MHz channel widths. Use higher channel widths only if you require very high application throughput demand in low density deployments with a small number of wireless devices.
Extension Channel
The extension channel controls whether the radio adds an extra 20 MHz of channel width above or below the selected channel.
Transmit Power
You can optionally set the maximum transmit power to limit or expand the transmission distance of your wireless signals. You can set the transmit power between 3dBm to 20dBm, or set the value to Auto.
The default (Auto) enables the Firebox to use the maximum transmit power allowed in the country of operation. The transmit power cannot exceed the regulatory limits set by your region.
We recommend that you set your transmit power to limit your coverage area so that it does not expand outside the necessary boundaries for your deployment.
Fragmentation Threshold
The Fragmentation Threshold is the maximum frame size the wireless Firebox can send and not fragment the frame. We recommend you use the default value. The default is the maximum frame size of 2346, which means that the Firebox will never fragment any frames that it sends to wireless clients.
RTS Threshold
RTS/CTS (Request To Send/Clear To Send) helps prevent problems when wireless clients receive signals from more than one wireless access point on the same channel. We recommend you use the default value. When the RTS Threshold is set to the default of 2346, RTS/CTS is disabled.
- To configure wireless threat detection and mitigation for WPA/WPA2 KRACK vulnerabilities, select the Advanced Settings tab.
- To block handshake messages that can potentially exploit clients and forces clients to reauthenticate, select the Enable WPA/WPA2 Vulnerability Mitigation check box. This option is disabled by default.
This re-authentication typically does not require the user to re-enter credentials, but it might add a few seconds to the connection time of the client. This mitigation logic can trigger for other similar dropped packet symptoms, for example, natural frame errors during a handshake, or dropped packets when a client roams. This can cause some client authentication connections to fail and reestablish.
WatchGuard recommends you enable this mitigation feature until you have updated all your client software to address the WPA/WPA2 client vulnerabilities, and evaluate the impact to your client environment and user experience.
- To save configuration changes to the cloud, click Save.