
Related Topics
Enable Active Directory Single Sign-On (SSO)
This procedure describes how to enable Active Directory Single Sign-On. For information about how to enable RADIUS Single Sign-On, see Enable RADIUS Single Sign-On.
Before you can enable Active Directory SSO, you must:
- Configure your Active Directory server
- Install the WatchGuard Single Sign-On (SSO) Agent and Event Log Monitor
- Install the WatchGuard Single Sign-On (SSO) Client (Optional)
- Install the WatchGuard Single Sign-On (SSO) Exchange Monitor (Optional)
If your device runs Fireware v11.0–v11.3.x, the Authentication Settings for Terminal Services are not available.
Enable and Configure SSO
When you enable and configure the settings for SSO on your Firebox, you must specify the IP address of the SSO Agent. You can also change the amount of time the SSO Agent caches data from an Active Directory server, specify the IP addresses (or ranges) to exclude from SSO queries, and enable SSO through the branch office VPN tunnels on your Firebox.
When you enable SSO through your BOVPN tunnels, SSO connections through the tunnel to your domain workstations can increase the bandwidth consumption of the tunnel.
- Select Authentication > Single Sign-On.
The Single Sign-On page appears. - Select the Enable Single Sign-On (SSO) with Active Directory check box.

- In the SSO Agent IP address text box, type the IP address of your SSO Agent.
- If you use AD Mode for SSO, in the Cache data for text box, specify the amount of time the SSO Agent caches data from an Active Directory server.
For more information about AD Mode, see About SSO. - In the SSO Exceptions list, add or remove the IP addresses or ranges to exclude from SSO queries.
- To enable users who connect to your network through a BOVPN tunnel to use SSO, select the Enable Single Sign-On (SSO) through BOVPN tunnels check box.
- Click Save to save your changes.
For more information about SSO exceptions, see the Define SSO Exceptions section.
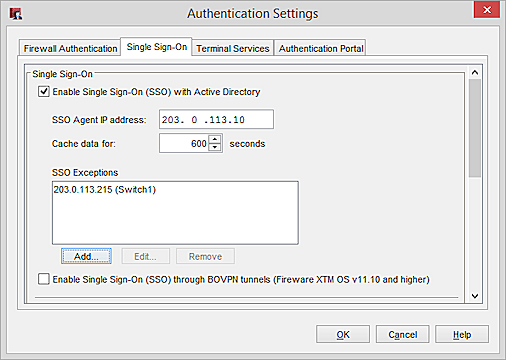
- Select Setup > Authentication > Authentication Settings.
The Authentication Settings dialog box appears. - Select the Single Sign-On tab.
- Select the Enable Single Sign-On (SSO) with Active Directory check box.

- In the SSO Agent IP address text box, type the IP address of your SSO Agent.
- If you use AD Mode for SSO, in the Cache data for text box, specify the amount of time the SSO Agent caches data from an Active Directory server.
For more information about AD Mode, see About SSO. - In the SSO Exceptions list, add or remove the IP addresses or ranges to exclude from SSO queries.
- To enable users who connect to your network through a BOVPN tunnel to use SSO, select the Enable Single Sign-On (SSO) through BOVPN tunnels check box.
- Click OK to save your changes.
For more information about SSO exceptions, see the Define SSO Exceptions section.
Define SSO Exceptions
If your network includes devices with IP addresses that do not require authentication, such as network servers, print servers, or computers that are not part of the domain, if you have users on your internal network who must manually authenticate to the Authentication Portal, or if you have terminal servers for the Terminal Services Agent, we recommend that you add their IP addresses to the SSO Exceptions list.
Each time a connection attempt occurs from an IP address that is not in the SSO Exceptions list, the Firebox contacts the SSO Agent to try to associate the IP address with a user name. This takes about 10 seconds. You can use the SSO Exceptions list to prevent this delay for each connection, to reduce unnecessary network traffic, and enable users to authenticate and connect to your network without delay.
When you add an entry to the SSO Exceptions list, you can choose to add a host IP address, network IP address, subnet,
- Click Add.
The Add IP Addresses dialog box appears. - From the Choose Type drop-down list, select the type of entry to add to the SSO Exceptions list:
- Host IP
- Network IP
- Host Range
The text boxes that appear change based on the type you select.
- Type the IP address for the type you selected.
If you selected the type Host Range, in the From and To text boxes, type the start and end IP addresses for the range. - (Optional) In the Description text box, type a description to include with this exception in the SSO Exceptions list.
- Click OK.
The IP address or range appears in the SSO Exceptions list. - Click Save.
- Below the SSO Exceptions list, click Add.
The Add SSO Exception dialog box appears.

- From the Choose Type drop-down list, select the type of entry to add to the SSO Exceptions list:
- Host IPv4
- Network IPv4
- Host Range IPv4
- Host Name (DNS lookup)

- In the Value text box, type the IP address for the type you selected.
If you selected the type Host Range, in the Value text box, type the IP address at the start of the range.
In the To text box, type the IP address at the end of the range.
- (Optional) In the Description text box, type a description to include with this exception in the SSO Exceptions list.
The Comment text box does not appear for the Host Name type. - Click OK.
The IP address or range appears in the SSO Exceptions list.
You can also edit or remove entries from the SSO Exceptions list.
- From the SSO Exceptions list, select an entry.
- Click Edit.
The Edit SSO exception IP dialog box appears. - Change the settings for the SSO exception.
- Click OK.
The updated entry appears in the SSO Exceptions list.

- Click OK.
- From the SSO Exceptions list, select an entry.
- Click Remove.
The selected entry is removed from the SSO Exceptions list. - Click Save.
- From the SSO Exceptions list, select an entry.
- Click Remove.
The selected entry is removed from the SSO Exceptions list. - Click OK.
See Also
About Active Directory Single Sign-On (SSO)
Choose Your Single Sign-On (SSO) Components
Install the WatchGuard Single Sign-On (SSO) Agent and Event Log Monitor
Install the WatchGuard Single Sign-On (SSO) Client
Install the WatchGuard Single Sign-On (SSO) Exchange Monitor
Troubleshoot Single Sign-On (SSO)
Use Authentication to Restrict Incoming Connections