BOVPN Virtual Interface for Static Routing to Microsoft Azure
You can configure static or dynamic routing. This topic covers static routing. For information about dynamic routing, go to BOVPN Virtual Interface for Dynamic Routing to Microsoft Azure.
Configuration Example
This example shows the configuration settings for a BOVPN virtual interface and static routing between a Firebox at Site A, and a Microsoft Azure virtual network at Site B. For detailed instructions, go to Configure a BOVPN virtual interface connection to a Microsoft Azure virtual network in the WatchGuard Knowledge Base.
Firebox Interfaces
For this example, the Firebox at Site A has one external interface and one trusted network.
Azure does not support VPN connections to Fireboxes behind NAT devices. The Firebox must have a public external IP address.
| Interface | Type | Name | IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | External | External | 203.0.113.2/24 |
| 1 | Trusted | Trusted | 10.0.1.1/24 |
Azure Interfaces
For this example, the Microsoft Azure virtual network at Site B has one external virtual interface and one trusted virtual network.
| Interface | Type | Name | IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | External | External | 198.51.100.2/24 |
| 1 | Trusted | Trusted | 10.0.100.1/24 |
Firebox Configuration
The Gateway Settings tab of the BOVPN virtual interface configuration uses these settings:
- The Remote Endpoint Type is Cloud VPN or Third-Party Gateway endpoint type, which supports wildcard traffic selectors and does not use GRE.
- The Credential Method is Pre-Shared Key and must use the pre-shared key the two sites agreed upon. Azure supports only the pre-shared key authentication method for site-to-site VPNs.
- The Gateway Endpoint settings are:
- Local Gateway: 203.0.113.2 (the IP address of the external interface on the Site A Firebox)
- Remote Gateway: 198.51.100.2 (the IP address of the external interface on the Site B Azure gateway)

Site A gateway configuration in Fireware Web UI

Site A gateway configuration in Policy Manager
The VPN Routes tab of the BOVPN virtual interface configuration uses these settings:
- Route to: 10.0.100.0/24

Site A static route configuration in Fireware Web UI

Site A static route configuration in Policy Manager
On the Phase 1 Settings tab, select these settings:
- Version — IKEv2. Static VPN routes between your Firebox and Azure require IKEv2.
- Authentication — Select an option that Microsoft Azure supports for Phase 1.
- Encryption — Select an option that Microsoft Azure supports for Phase 1.
- Key Group — Select a Diffie-Hellman group that Microsoft Azure supports for Phase 1.
For information about Microsoft cryptographic requirements, go to About VPN devices and IPsec/IKE parameters for Site-to-Site VPN Gateway connections and About cryptographic requirements and Azure VPN gateways in the Microsoft documentation.
The default Key Group setting is Diffie-Hellman Group 14.

Site A Phase 1 settings in Fireware Web UI

Site A Phase 1 settings in Policy Manager
On the Phase 2 Settings tab, select these settings:
- Perfect Forward Secrecy — Yes
- Diffie-Hellman — Select a Diffie-Hellman group that Microsoft Azure supports for Phase 2.
- IPSec proposal — Select a proposal that Microsoft Azure supports for Phase 2.
For information about Microsoft cryptographic requirements, go to About VPN devices and IPsec/IKE parameters for Site-to-Site VPN Gateway connections and About cryptographic requirements and Azure VPN gateways in the Microsoft documentation.
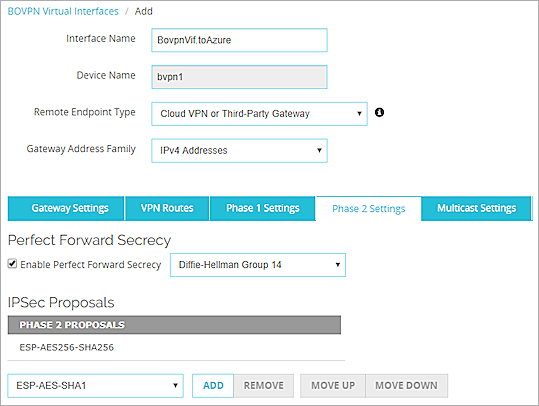
Site A Phase 2 settings in Fireware Web UI
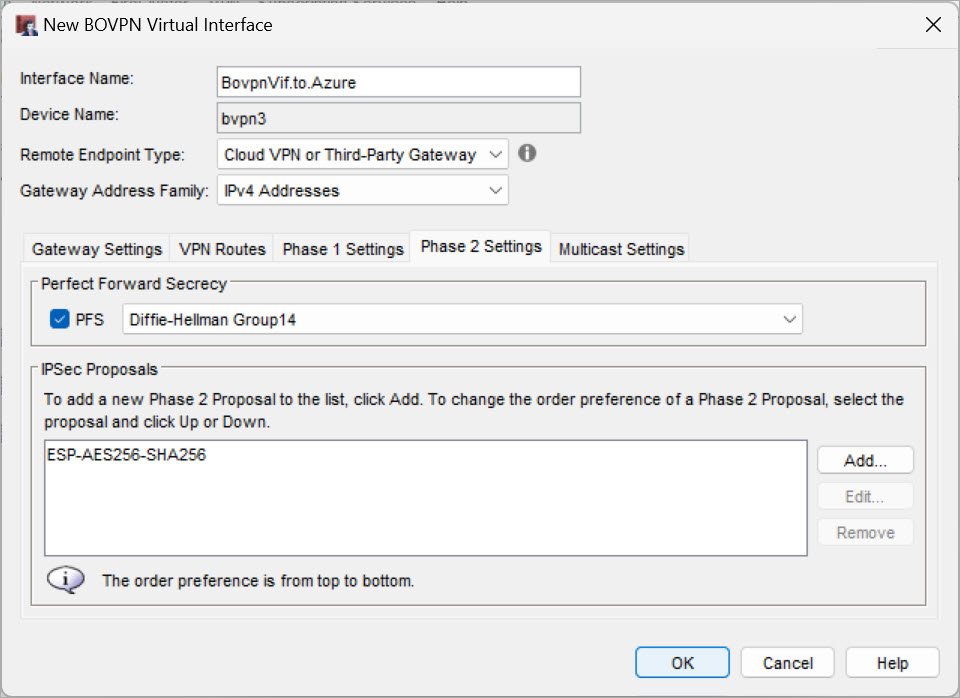
Site A Phase 2 settings in Policy Manager
Site B BOVPN Virtual Interface Configuration
On your Microsoft Azure virtual network, the gateway settings are:
- Remote gateway: 203.0.113.2 (the IP address of the first external interface on the Firebox at Site A )
- Local gateway: 198.51.100.2 (the IP address of the external interface on the Azure gateway at Site B )
- VPN route: 10.0.1.0/24 (the IP address of the Site A network)
MTU Settings
For Azure VPN connections, Microsoft requires a maximum TCP MSS of 1350 or MTU of 1400. The Azure VPN gateway drops packets with a total packet size larger than 1400.
If the Azure VPN gateway drops packets from your Firebox, we recommend these Firebox settings:
- Fireware v12.5 or higher — In the BOVPN virtual interface configuration, specify an MTU of 1400. For more information about the MTU setting, go to Configure a Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) Value.
- Fireware v12.4.1 or lower — In the physical interface configuration, specify an MTU of 1400.
As an alternative, you can set the global TCP MSS value to 1350. However, we do not recommend this option because this setting affects other Firebox interfaces and applies only to TCP traffic. For example, this setting does not apply to RDP traffic in most cases because RDP usually uses UDP. If you use RDP to access servers hosted in Azure, Azure will drop packets larger than 1400 bytes even if you specify the recommended TCP MSS value. For more information about the TCP MSS setting, go to Define Firebox Global Settings.
For more information about Azure configuration settings, go to the documentation provided by Microsoft.
BOVPN Virtual Interface for Dynamic Routing to Microsoft Azure
Configure a BOVPN Virtual Interface