We recommend that the Firebox external interface has a public IP address. If the external interface of your Firebox has a private IP address because your ISP does Network Address Translation (NAT) or because your Firebox is connected to a device that does NAT, a remote VPN device cannot use that private IP address for VPN connections to the Firebox.
However, you can still configure VPN tunnels because the Firebox can use NAT traversal (NAT-T). This topic explains how to configure BOVPN tunnels when the NAT device the Firebox connects to has a dynamic or static public IP address.
Requirements
Ports
Devices that do NAT usually have some basic firewall features. To make a VPN tunnel to your Firebox when the Firebox is installed behind a device that does NAT, the NAT device must let the traffic through. These ports and protocols must be open on the NAT device:
- UDP port 500 (IKE)
- UDP port 4500 (NAT Traversal)
NAT Traversal (NAT-T)
You must enable NAT-T on the Firebox and the other VPN endpoint device. With NAT-T enabled, the Firebox and the other VPN endpoint device can detect the NAT device and switch data packets from raw ESP to ESP encapsulated within UDP 4500 packets. The encapsulated packets can then be NATed.
In a pcap packet capture of this traffic, you would see only UDP 500 traffic, which occurs during BOVPN setup, followed by UDP 4500 traffic for all data packets.
You do not need to specify private IP addresses in the Phase 1 settings on the Firebox or on the other VPN endpoint device. The next section shows how to specify a gateway ID that is not an IP address.
If the NAT device that the Firebox connects to has a dynamic public IP address
In this case, we recommend one of these two options:
- About the Dynamic DNS Service.
- Configure the General Settings for a BOVPN gateway.
- In the Phase 1 settings of the BOVPN gateway configuration, select NAT Traversal.
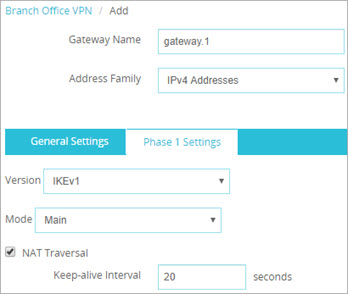
Phase 1 settings in the Web UI
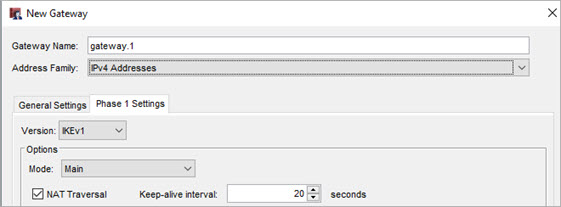
Phase 1 settings in Policy Manager
- Define Gateway Endpoints for a BOVPN Gateway and specify this option for the gateway ID:
- In the Web UI, select By Domain Name.
- In Policy Manager, select By Domain Information.
- Type the domain name of the dynamic DNS service provider as the Local ID. The remote device must identify your Firebox by domain name and it must use the domain name of the dynamic DNS service provider associated with your Firebox.
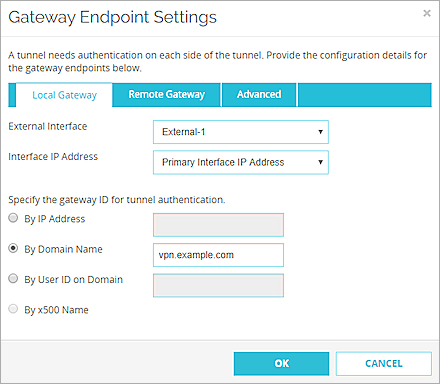
Gateway Endpoint settings in the Web UI
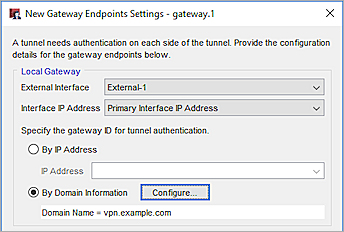
Gateway Endpoint settings in Policy Manager
- Configure all other BOVPN settings as specified in Define Gateway Endpoints for a BOVPN Gateway.
- Configure Manual BOVPN Tunnels.
You can specify any type of gateway ID and any gateway ID, but the local and remote gateway IDs must correspond as follows:
- The local gateway ID on Firebox A and the remote gateway ID on Firebox B must match.
- The local gateway ID on Firebox B and the remote gateway ID on Firebox A must match.
- About the Dynamic DNS Service.
- Configure the General Settings for a BOVPN gateway.
- In the Phase 1 settings of the BOVPN gateway configuration, select NAT Traversal.
- Define Gateway Endpoints for a BOVPN Gateway and specify this option for the gateway ID:
- In the Web UI, select By Domain Name.
- In Policy Manager, select By Domain Information.
- In the adjacent text box, type the letters, numbers, or characters to use for the gateway ID. For example, you could type the name test.
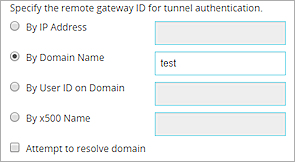
Gateway Endpoint settings in the Web UI
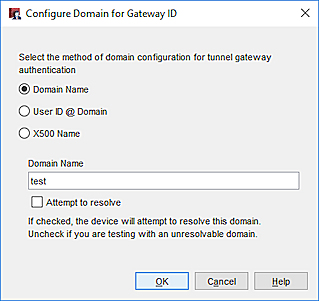
Gateway ID Domain settings in Policy Manager
Gateway Endpoint settings in the Policy Manager
- Configure all other BOVPN settings as specified in Define Gateway Endpoints for a BOVPN Gateway.
- Configure Manual BOVPN Tunnels.
As a best practice, traffic should always be generated from the devices that are protected by the NAT-T firewall. The Firebox that is behind the NAT device with a dynamic public IP address must initiate the VPN connection if the NAT device is assigned a new IP address. This is required so the remote device knows how to contact the Firebox.
If the NAT device that the Firebox connects to has a static public IP address
For a VPN connection to a remote Firebox behind a NAT device, specify the static public IP address of the NAT device in the VPN connection settings.
For example, you have two Fireboxes A and B. Firebox B is behind a NAT device that has a static public IP address of 192.0.2.1. In the Remote Gateway Endpoint Settings for Firebox A, specify the IP address 192.0.2.1.
For the gateway ID, specify any data that is not a resolvable domain name. For example, you could type test or ID-123. You can specify any type of gateway ID and any gateway ID, but the local and remote gateway IDs must correspond as follows:
- The local gateway ID on Firebox A and the remote gateway ID on Firebox B must match.
- The local gateway ID on Firebox B and the remote gateway ID on Firebox A must match.
Configuration
For a Firebox behind a NAT device with a static public IP address, configure these BOVPN settings:
- About the Dynamic DNS Service
- Configure the General Settings for a BOVPN gateway.
- In the Phase 1 settings of the BOVPN gateway configuration, select NAT Traversal.
- Define Gateway Endpoints for a BOVPN Gateway and specify this option for the remote gateway ID:
- In the Web UI, select By Domain Name.
- In Policy Manager, select By Domain Information.
- Specify a non-resolvable gateway ID.
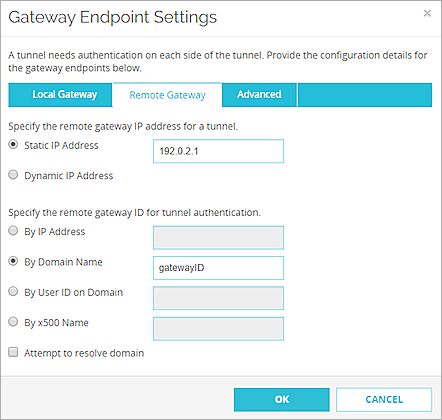
Remote Gateway Endpoint settings in the Web UI
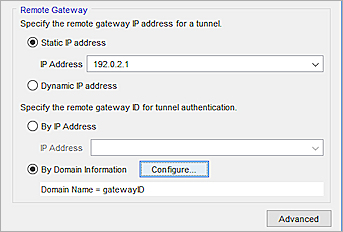
Remote Gateway Endpoint settings in the Policy Manager
- Configure all other BOVPN settings as specified in Define Gateway Endpoints for a BOVPN Gateway.
- Configure Manual BOVPN Tunnels.
Configure Manual BOVPN Gateways
Configure a BOVPN to a Locally-Managed Firebox or Third-Party VPN Endpoint