Enable a Wireless Guest Network
To enable a wireless network for guest users, we recommend you configure an access point in the custom zone and use the wireless interface alias when you configure policies for traffic from guest wireless clients.
By default, traffic for a custom interface is not allowed through the Firebox unless you specifically configure policies to allow it. You must create policies to allow guest wireless users access. For more information, go to Wireless Guest and Policies.
For more information on the custom zone, go to Configure a Custom Interface.
- Select Network > Wireless.
The Wireless Configuration page appears.

- Select Enable wireless access points.
- Adjacent to an access point, click Configure.
The Access Point Configuration dialog box appears.

- Select the Enable Access Point x check box.
For example, if you selected access point 1, select the Enable Access Point 1 check box. - In the Interface Name (Alias) text box, you can change the alias name of the interface or use the default name.
- From the Interface Type drop-down list, select Custom.
- In the IP Address text box, type the private IP address to use for the wireless guest network.
The IP address you specify must not already be in use on one of your network interfaces. - To configure the Firebox as a DHCP server when a wireless device tries to make a connection, from the drop-down list, select DHCP Server.
- Select the Wireless tab.
The Wireless settings appear with the security settings for the wireless guest network.

- To make your wireless guest network name visible to guest users, select the Broadcast SSID check box.
- To send a log message each time a wireless computer tries to connect to the guest wireless network, select the Log authentication events check box.
- To require wireless users to use the WatchGuard Mobile VPN with IPSec Client , select the Require encrypted Mobile VPN with IPSec connections for wireless clients check box.
When you select this option, the Firebox only allows DHCP, DNS, IKE (UDP port 500), and ESP packets over the wireless network. This can increase the security for wireless clients if you do not select WPA or WPA2 as the wireless authentication method.
- Select the Radio (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, or both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) that will broadcast this SSID.
- In the Network name (SSID)) text box, specify a unique name for your wireless guest network or keep the default name.
- From the Security drop-down list, select the encryption and authentication setting to enable for wireless connections to the optional interface. For more information, go to Set the Wireless Security Method.
- From the Encryption algorithm drop-down list, select the encryption algorithm to use.
- In the Passphrase text box, specify the keys or passphrase required for the type of encryption you select.
If you select an authentication option that uses pre-shared keys, a random pre-shared key is generated for you. You can use this key or specify a new key. - Click Return to Main Page.
- Click Save.
Make sure you configure your Firebox policies to allow access for this Guest network. By default, a Guest wireless network in the custom zone has no access policies. For more information, go to Wireless Guest and Policies.
- Select Network > Wireless.
The Wireless Configuration dialog box appears.
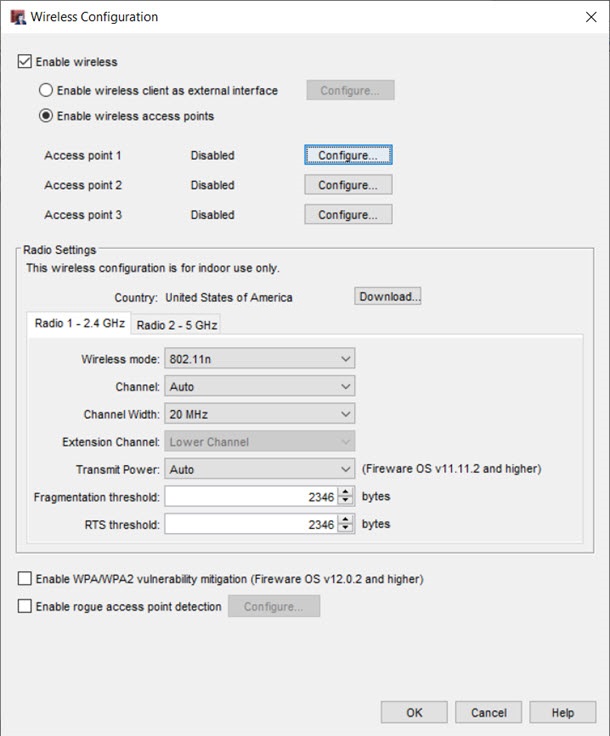
- Select the Enable wireless check box.
- Select Enable wireless access points.
- Adjacent to an access point, click Configure.
The Access Point Configuration dialog box appears.

- In the Interface Name (Alias) text box, you can change the alias name of the interface or use the default name.
- From the Interface Type drop-down list, select Custom.
- In the IP Address text box, type the private IP address to use for the wireless guest network.
The IP address you specify must not already be in use on one of your network interfaces. - To configure the device as a DHCP server when a wireless device tries to make a connection, select Use DHCP Server.
- Select the Wireless tab.
The Wireless settings appear with the security settings for the wireless guest network.

- To make your wireless guest network name visible to guest users, select the Broadcast SSID check box.
- To send a log message each time a wireless computer tries to connect to the guest wireless network, select the Log authentication events check box.
- To require wireless users to use the WatchGuard Mobile VPN with IPSec Client , select the Require encrypted Mobile VPN with IPSec connections for wireless clients check box.
When you select this option, the device only allows DHCP, DNS, IKE (UDP port 500), and ESP packets over the wireless network. This can increase the security for wireless clients if you do not select WPA or WPA2 as the wireless authentication method.
- Select the Radio (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, or both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) that will broadcast this SSID.
- In the Network name (SSID)) text box, type a unique name for your wireless guest network or keep the default name.
- From the Security drop-down list, select the encryption and authentication to enable for wireless connections to the optional interface. For more information, go to Set the Wireless Security Method.
- From the Encryption algorithm drop-down list, select the encryption algorithm to use.
- In the Passphrase text box, specify the keys or passphrase required for the type of encryption you select.
If you select an authentication option that uses pre-shared keys, a random pre-shared key is generated for you. You can use this key or type a new key. - Click OK.
- Save the configuration.
Make sure you configure your Firebox policies to allow access for this Guest network. By default, a Guest wireless network in the custom zone has no access policies. For more information, go to Wireless Guest and Policies.
You can also configure your wireless guest network as a hotspot. For more information, go to Configure a Hotspot.
You can also restrict access to the guest network by MAC address.
- To enable MAC access control, select the MAC Access Control tab.
- Configure the settings as described in Restrict Network Traffic by MAC Address.
Wireless Guest and Traffic Management
You can use Traffic Management on a policy for your wireless networks. This feature enables you to control the amount of bandwidth used by wireless guest networks to prevent wireless guest clients from using too many resources.
For more information on Traffic Management, go to About Traffic Management and QoS.
Wireless Guest and Policies
You can use the custom zone interface type for your wireless interface. Because a custom interface is not included in the list of built-in aliases, traffic for a custom interface is not allowed through the Firebox unless you specifically configure policies to allow it. This is important for wireless guest network security to make sure users cannot access a trusted or optional network.
For example, to allow the GW-Wireless-Guest wireless interface outbound access from the Firebox, you must add the interface to the From field of the Outgoing policy for the Firebox.
For wireless guest policies, we recommend that you create a new alias named Any-Guest. You can then use the Any-Guest alias in policies for your wireless guest network. For more information, go to Create an Alias.