What role does blockchain play in cyberattacks and cybersecurity?

Most company decision-making executives know how blockchain technology works but few have adopted it within their organization at this stage. This is the conclusion drawn by the latest Pulse survey conducted on 145 senior IT managers from companies on three continents. It shows that only 8% have experienced this technology, compared to 53% who know how it works but are yet to use it.
Only 9% of organizations claim to have fully implemented blockchain-based solutions in their core business, while 78% plan to use it on an occasional basis. "Blockchain in business still has a long way to go. We won’t see any major moves until 2024, in my opinion," states the director of one of the SMEs in the FMCG sector who was consulted.
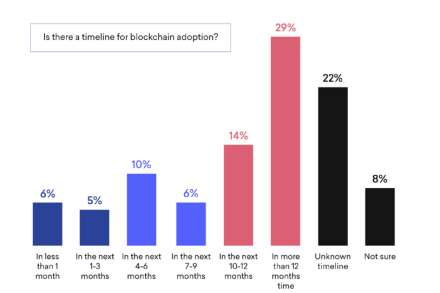
As regards those companies that have not yet used blockchain but are planning to adopt it, only 4 out of 10 businesses will do so in the next 12 months, while the rest state they have no timeline, or it will be a long-term plan.
Despite the fact that in 2016 technology and financial organizations invested close to one billion dollars in this technology, with the prospect of investing more over the following five years, blockchain technology has not taken off yet. In relation to this unfulfilled promise, the survey notes that 36% of companies that have already adopted blockchain think that it is still "too soon" to assess whether it is generating results.
And in terms of cybersecurity, is it a secure and cost-effective solution for businesses? According to the C-Suite of a major financial institution that participated in the survey: "After announcing that we were accepting cryptocurrencies, we saw a huge increase in the number of cyberattacks on our company. Luckily, we have a very mature security infrastructure. However, I think smaller businesses without a solid cybersecurity infrastructure could open themselves up to large problems."
In this regard, MIT Technology Review noted that in 2019 technology that a priori was 100% secure was now getting hacked. Hackers stole around $2 billion in cryptocurrencies from 2017 to 2019, while criminal organizations accessed the blockchain exchange network and "heisted" another $1.1 billion in this same time period.
Despite the fact that adoption of blockchain has not been as widespread as expected, the leaders consulted say the top business cases for blockchain will be managing access to the main network and improving efficiency in business processes (62%), above other uses such as cross-border payments (40%), asset tracking (39%), generating smart contracts (39%), data management (38%) and helping in the supply chain (37%). In addition, 85% believe that blockchain technology will end up playing a crucial role in the future of their business.
WatchGuard believes blockchain is a very valuable technology in multiple industries such as banking, healthcare or the public sector, but its use in cybersecurity is still limited. It is effective in identifying access to endpoints, in knowing what has happened and who has done this, but there is still much to be explored. Solutions that rely on multi-factor authentication strengthen organizations' access points and make up for the shortcomings that blockchain still suffers from in this regard.


