Applies To: WatchGuard Cloud-managed Access Points (AP130, AP230W, AP330, AP332CR, AP430CR, AP432)
You can use VLANs (Virtual LANs) with your Wi-Fi in WatchGuard Cloud access points. If you have several access points connected to the same physical network, you can use VLANs to logically separate traffic between SSIDs.
For example, you can create VLANs to separate the traffic of the private trusted Wi-Fi network and the guest Wi-Fi network, or separate traffic based on your existing wired network VLANs.
VLANs enable you to improve security, manage access, and reduce broadcast traffic for your networks.
About Dynamic VLANs
With access point firmware v2.2 or higher and WPA2 or WPA3 Enterprise authentication, you can also use Dynamic VLANs that enables you to dynamically assign VLANs to a wireless client based on the information returned about the user from a RADIUS server after successful authentication.
This reduces the management required to assign connections to specific VLANs because the VLANs are assigned automatically based on the user or group membership of the user on your RADIUS server, such as an Active Directory NPS (Network Policy Server).
For more information, go to Configure Access Point Dynamic VLANs.
About VLAN Configuration
A VLAN can by tagged or untagged. A tagged VLAN uses a specific VLAN ID that is added to a network packet, based on the IEEE 802.1Q standard. This VLAN ID enables the traffic to be correctly handled by network switches or other network devices that have 802.1Q VLAN tagging enabled on their ports. The network traffic can only be communicated to other ports on the switch that are configured with that VLAN ID.
An untagged VLAN means the network traffic is not assigned a specific VLAN ID. When the untagged traffic reaches the network switch or other gateway device, the traffic is handled as part of the default or native VLAN, such as VLAN 0, and can be communicated to any other port on the device to other network switches or devices.
If you enable VLAN tagging for SSIDs on a WatchGuard access point, or you enable a tagged management VLAN for an access point, you must also enable VLANs on the network switch, Firebox, or other gateway device that the access point connects to.
In the default configuration when you add an access point to WatchGuard Cloud, the access point requires an untagged VLAN to connect to the network and communicate with WatchGuard Cloud.
- For more information about how to configure VLAN tagging on a network switch, go to Configure VLANs on a Managed Network Switch.
- For more information about VLANs on a Firebox, go to Configure VLANs on a Firebox.
- For more general information on VLANs, Tagging, and WatchGuard Fireboxes, go to About Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs).
Wireless Network VLAN Example
To separate traffic between your private and guest Wi-Fi networks, you can assign these VLAN IDs for access point management traffic and for your private and guest wireless SSIDs:
- Management VLAN — In most environments, access point management VLAN traffic is typically untagged to prevent disconnection of access points from wireless management access. In the default configuration when you add an access point to WatchGuard Cloud, the access point requires a connection to an untagged VLAN network to connect to the Internet and communicate with WatchGuard Cloud.
If you want to use a tagged management VLAN for your access point deployment, make sure the access point is already connected to the network and communicates with WatchGuard Cloud on an untagged VLAN before you change the management VLAN to a tagged VLAN.
In this example, we use VLAN ID 10 for management communications to the access point.
- Private Wi-Fi Network (VLAN ID 20) — Tagged VLAN for the private SSID for wireless connections to your trusted network.
- Guest Wi-Fi Network (VLAN ID 30) — Tagged VLAN for the guest SSID for wireless guest access to the Internet.
Configure a Management VLAN on an Access Point
Before you configure a tagged VLAN for management communications to an access point, make sure that the access point can initially connect to the network and Internet from an untagged VLAN network.
In its default configuration, the access point requires a connection to an untagged VLAN network to connect to WatchGuard Cloud to receive a configuration.
To configure a tagged VLAN for management communications to an access point, from WatchGuard Cloud:
- Connect the access point to a network with an untagged VLAN that has access to the network and the Internet.
This enables the access point to maintain a connection to the network after it receives the configuration from WatchGuard Cloud. - Select Configure > Devices.
- Select a cloud-managed access point.
- Select Device Configuration.
- From the Settings tile, select Device Settings.

- Select the Enable Management VLAN check box.
- Select a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094.
In this example, we use VLAN 10. - Click Save.
- Deploy the configuration to the access point.
If your untagged management VLAN network does not have access to the Internet, you must manually configure the access point VLAN settings for the management VLAN from the access point CLI (Command Line Interface). When you save the configuration to the access point from the CLI and the device is configured on the correct VLAN, the device can then connect to WatchGuard Cloud and receive the cloud configuration. For more information, go to Access Point Command Line Interface.
- Update your network devices, such as your network switch, Firebox, or other network devices, to use the same tagged VLAN ID.
Configure VLANs on an SSID
To configure a tagged VLAN on a wireless network SSID, from WatchGuard Cloud:
- Select Configure > Devices.
- Select a cloud-managed access point.
- Select Device Configuration.
- From the Wi-Fi Networks tile, select SSIDs.
- Select an existing SSID for your private Wi-Fi network, or create a new SSID.
- In the Network section of the wireless configuration, select the Enable VLAN check box.
- Select a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094.
In this example, we use VLAN 20 for the private Wi-Fi network.
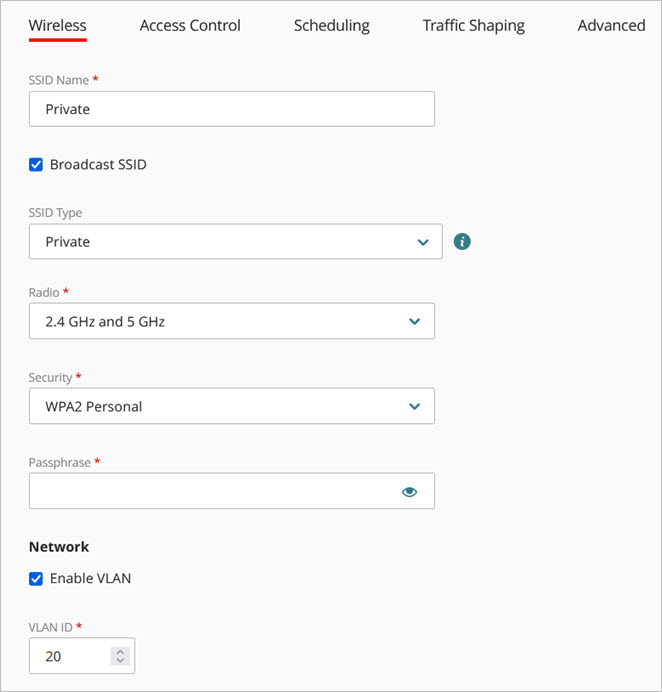
- Click Save.
- Repeat these steps to set the VLAN ID for your guest Wi-Fi network to 30.

- Deploy the configuration to the access point.
- Update your network devices, such as your network switch, Firebox, or other network devices, to use the same tagged VLAN IDs.
Configure VLANs on a Firebox
If you connect your access point to a Firebox interface, you must configure VLANs on the Firebox interfaces to enable VLAN tagging for your SSIDs.
For the Firebox interface where you connect your access point, set the Interface Type to VLAN. Then, configure the VLANs to use for the access point.
For information about how to create a VLAN on a Firebox, go to Configure Firebox VLANs.
- Configure the VLANs on the Firebox that each SSID uses to send tagged traffic to the VLAN interface.
- If your access point management connection is configured as an untagged VLAN (no Management VLAN ID configured), configure a VLAN on the Firebox that the access point management connection uses to send untagged traffic to the VLAN interface.
- If you enable a tagged management VLAN for your access point, configure a VLAN on the Firebox that the access point management connection uses to send tagged traffic to the VLAN interface.
- Enable DHCP server or DHCP relay on each VLAN.
- The access point gets an IP address from the DHCP server on the VLAN used for management communications.
- Wireless clients that connect to an SSID get an IP address from the DHCP server on the VLAN for that SSID.
Configure VLANs on a Managed Network Switch
If you enable VLAN tagging and want to connect your access point to a managed switch, you must also configure VLANs on the switch. The switch must support 802.1Q VLAN tagging.
On the switch, you must:
- Add VLANs with the same IDs as the VLANs you configured on the access point and SSIDs.
- Configure the switch interfaces that connect to the access point to send and receive tagged traffic for the VLANs assigned to each SSID.
- If you enable a tagged management VLAN for your access point, configure the switch interfaces that connect to the access point to send and receive tagged traffic for access point management.
See the documentation for your network switch for instructions to enable and configure the VLANs on your switch.
If you have enabled VLAN tagging in the SSIDs on your access point, do not connect your access point to a switch that does not support 802.1Q VLAN tagging.