Applies To: AuthPoint Multi-Factor Authentication, AuthPoint Total Identity Security
This topic includes recommendations and best practices to help you configure and deploy AuthPoint multi-factor authentication (MFA). Each section describes some of the requirements and commonly missed steps required to set up AuthPoint.
This is not a comprehensive guide. For complete and detailed steps to configure AuthPoint, see the help topics for each integration.
Policies and Policy Objects
When you configure policies, make sure you follow these requirements and recommendations:
- For RADIUS authentication and basic authentication (ECP), policies that have a network location or geofence do not apply because AuthPoint does not have the IP address of the end user or the origin IP address.
- You must enable the push authentication method for policies with MS-CHAPv2 RADIUS resources.
- RADIUS resources do not support QR code authentication.
When you add a policy object to an authentication policy, the policy only applies to user authentications that match the conditions of the authentication and the policy objects. For example, if you add a specific network location to a policy, the policy only applies to user authentications that come from that network location.
We recommend that you create a second policy for the same groups and resources without the policy object. Users who only have a policy that includes a policy object do not get access to the resource when the conditions of the policy object do not apply to the authentication (because they do not have a policy that applies, not because authentication is denied).
- Users who only have a policy that includes a network location do not get access to the resource when they authenticate outside of that network location.
- Users who only have a policy that includes a time schedule do not get access when they authenticate outside the hours of that time schedule.
- Users who only have a policy to allow access that includes a geofence do not get access to the resource when they authenticate outside of the specified countries.
External Identities
Do not add the same LDAP group to multiple group syncs or create multiple group syncs that include the same LDAP user. A user synced from an LDAP database cannot belong to more than one local AuthPoint group. If an LDAP user belongs to multiple group syncs, each time AuthPoint syncs with your LDAP database, the local AuthPoint group that the user belongs to might change.
For example, you configure two group syncs in AuthPoint:
- Group Sync 1
- LDAP Groups to Sync: Sales
- AuthPoint Group to Add Users To: Group A
- Group Sync 2
- LDAP Groups to Sync: Marketing
- AuthPoint Group to Add Users To: Group B
With this configuration, users that belong to both the Sales and Marketing LDAP groups will move between Group A and Group B each time AuthPoint syncs with your external identity provider. The AuthPoint group that the user belongs to depends on which group sync runs last.
To add LDAP users to multiple groups in AuthPoint, enable the Create new synchronized groups toggle in your group sync and use your Active Directory group structure to manage your users.
Sync Users from an Active Directory
To sync users from Active Directory, you must add an external identity in AuthPoint and install the AuthPoint Gateway.
When you configure an external identity:
-
If your Active Directory instance does not use LDAPS, you must disable the LDAPS toggle for the external identity. When you do this, the default port changes from 636 to 389.
- We recommend that you use the group sync feature to sync your users because it is easier to configure than an advanced query and, for Active Directory, you can choose to create new groups in AuthPoint based on the Active Directory groups that you sync users from.
- Do not add the same LDAP group to multiple group syncs or create multiple group syncs that include the same LDAP user. To add LDAP users to multiple groups in AuthPoint, we recommend that you enable the Create new synchronized groups toggle in your group sync and use your Active Directory group structure to manage your users.
- If you enable the Create new synchronized groups option, we recommend that you sync all of your Active Directory groups to AuthPoint and use the synced groups rather than AuthPoint groups when you configure your authentication policies.
- If you create a new Microsoft 365 user account and immediately sync the user from Active Directory, the mailbox for that user account might not be active when AuthPoint sends the token activation email to the user. In this scenario, the token activation email is not delivered and the email address is added to a block list in AuthPoint. We recommend that the user activates their token from the IdP portal (see Activate a Token).
- Do not configure multiple external identities for the same domain.
For more information about external identities, see About External Identities. For detailed instructions to configure an external identity and sync users from Active Directory or an LDAP database, see Sync Users from Active Directory or LDAP.
Sync Users from Azure Active Directory
When you sync users from Azure AD, be aware of these recommendations and requirements:
- When you create a group sync, we recommend that you enable the Create new synchronized groups option to create new groups in AuthPoint based on the Azure Active Directory groups that you sync users from and use the synced groups rather than AuthPoint groups when you configure your authentication policies.
- Do not add the same Azure AD group to multiple group syncs or create multiple group syncs that include the same Azure AD user. To add Azure AD users to multiple groups in AuthPoint, we recommend that you enable the Create new synchronized groups toggle in your group sync and use your Azure Active Directory group structure to manage your users.
- Azure AD users must log in to an Azure application to update their password before they can authenticate to AuthPoint resources (the applications and services that require MFA).
- Azure AD users can only use the Logon app if the Windows computer is part of the Azure domain.
- You do not need to install the AuthPoint Gateway to sync users from Azure AD.
- Because of a Microsoft limitation, Microsoft 365 only supports AuthPoint MFA for Azure AD users if they are synced with a local AD server. Microsoft 365 does not support MFA for users that only exist in Azure AD. For more information, see this Knowledge Base article.
- If Azure AD users get an error message that says “MFA did not authorize” when they authenticate to protected resources, this message usually comes from Azure Active Directory and indicates that AuthPoint could not validate the user credentials. We recommend that you add the AuthPoint Azure AD Integration IP addresses as Trusted IP addresses Azure Active Directory (Microsoft Entra). The Trusted IPs feature in Azure is based on your Azure subscription, and might not be available to all accounts. Additional configuration might be necessary if you have made changes to the default Microsoft Conditional Access Policies.
For detailed instructions to sync users from Azure AD, see Sync Users from Azure Active Directory.
AuthPoint Gateway
The Gateway uses TCP service ports 9000—9003 for internal communication between the different Gateway services. If other applications use these TCP service ports, the Gateway might fail to start or appear offline. Before you install the Gateway, make sure that the necessary ports are open and not in use.
To verify ports are not in use, you can use command prompt to run the command Netstat -ano |findstr 900. This command finds anything that begins with 900.
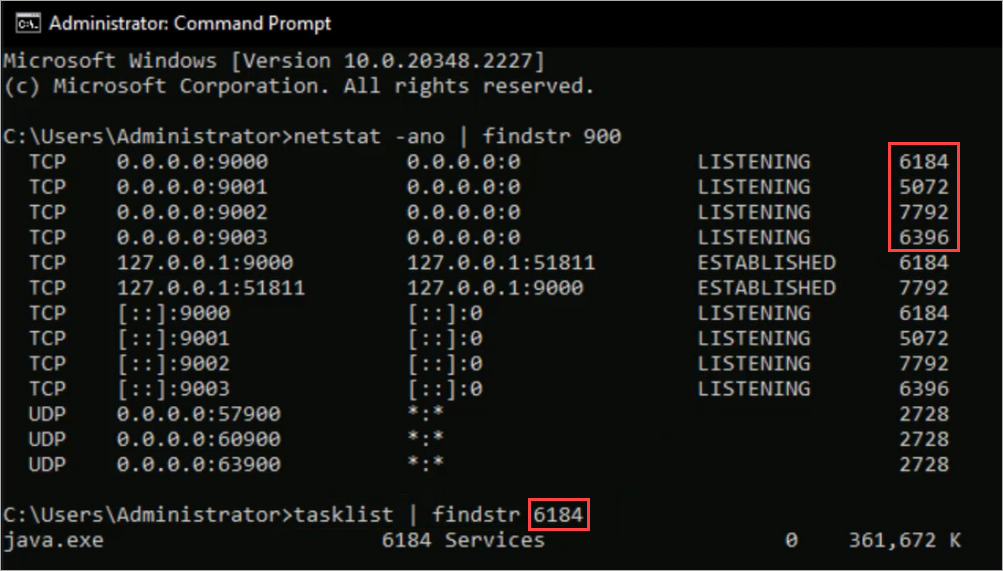
If one of the necessary ports is in use, you can run the command Tasklist | findstr process ID to identify which process is using that particular port.
When you use the tasklist command, the AuthPoint Gateway is java.exe. You can expect to see that if you already have a Gateway installed.
MFA for Microsoft 365
When you configure AuthPoint MFA for Microsoft 365, be aware of these recommendations and requirements:
- To use AuthPoint MFA (SAML), your Microsoft 365 domain must be federated. When your Microsoft 365 domain is federated, Microsoft 365 forwards user logins for that domain to the identity provider (AuthPoint) for authentication.
- To use Microsoft 365, each user must have an AuthPoint license and an AuthPoint user account.
- Service accounts must have a corresponding AuthPoint user account (this requires an AuthPoint license for the service account). If you want your service accounts to bypass MFA, you must configure an authentication policy with basic authentication that only requires password authentication.
AuthPoint automatically generates a token for service account users, but you do not have to activate or use the token because the service account will bypass MFA with basic authentication.
- If you have older client applications (for example, applications based on SMTP, POP, or IMAP) or if you have devices that are part of the Microsoft 365 domain but do not have a UI (such as a printer), you must enable the Basic Authentication toggle when you configure an authentication policy for your Microsoft 365 resource.
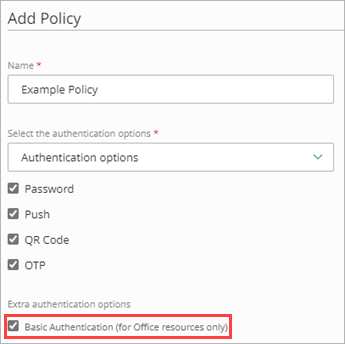
- To stagger the implementation of AuthPoint MFA for Microsoft 365, you can add users to different groups in AuthPoint and configure the authentication policies to require only a password for one group and MFA for another group. As you roll out AuthPoint, move users from the first group (password only) to the second group (MFA with push, OTP, or QR code).
We recommend that you create a comprehensive communication plan to explain to your users how to use MFA and what steps they must complete. To introduce AuthPoint to end users, see AuthPoint for End-Users
For detailed steps to configure AuthPoint MFA for Microsoft 365, see Office 365 Integration with AuthPoint.
MFA for ADFS
The AuthPoint ADFS agent adds MFA to ADFS for additional protection.
- If you use ADFS, we recommend that you install the AuthPoint ADFS agent to add the additional protection of MFA.
- If you do not already use ADFS, it might not make sense to deploy ADFS to use only with AuthPoint MFA. ADFS requires servers, licenses, and maintenance.
ADFS provides more flexibility for you to add MFA to on-premise applications and configure different rules for different groups of users. For example, with ADFS you can add MFA to Microsoft 365 for specific Active Directory groups. Unlike the SAML integration, you do not have to purchase licenses for users that belong to other groups.
For detailed instructions to configure AuthPoint MFA for ADFS, see Configure MFA for ADFS.
If you want to use ADFS to protect Exchange and also use AuthPoint MFA to protect ADFS logins, you must configure the Exchange organization to use ADFS authentication. For more information, see Step 6 in the Microsoft documentation.
MFA for Computers and Servers
The Logon app enables you to require MFA when users log in to a computer or server. This includes protection for RDP and RD Gateway.
Before you install the Logon app, make sure that:
- Users can log in to the computer or server you will install the Logon app on.
- Users have an AuthPoint user account and an active AuthPoint token.
When you set up and deploy the Logon app:
- The computer you install the Logon app on must be connected to the Internet when you log in for the first time.
- You can use a Windows command prompt to install the Logon app remotely on multiple computers through an Active Directory Group Policy Object (GPO).
- When you install the Logon app, MFA is required for local and remote access.
- If you use RD Gateway for remote connections, to require MFA you must install the Logon app on the computers that users connect to. To allow users to log in locally without MFA, configure your company network as a Network Location and configure a new policy for the Logon app resource with the Network Location policy object added.
For detailed instructions to configure and install the Logon app, see Configure MFA for a Computer or Server.
MFA for RD Web
The AuthPoint agent for RD Web adds the protection of MFA to RD Web Access. When you configure the agent for RD Web, users must authenticate to access the RD Web page.
- After you install or upgrade the agent for RD Web, we recommend that you reboot the server.
- When the user selects an application on the RD Web Access page, the behavior is different based on the web browser:
- Internet Explorer — When the user selects an application it opens directly in the browser.
- Other browsers — When the user selects an application, an .rdp file downloads. The user must run the .rdp file and type their login credentials to access the application.
Connections through an .rdp file are not protected by MFA. To require MFA for direct access to these applications, we recommend that you install the Logon app on servers that host the applications.
For detailed instructions to configure and install the AuthPoint agent for RD Web, see About the AuthPoint Agent for RD Web.
Network Access Enforcement
If you use AuthPoint multi-factor authentication at the same time as Network Access Enforcement, we recommend you use an alternate form of authentication, such as OTP (one-time password) or QR code instead of the Push method. The Push method might not work correctly if the client has not yet passed Network Access Enforcement validation to connect to the network. After the client has successfully passed the validation, subsequent authentication attempts can use the Push method.
Access Portal Certificate Expiration with AuthPoint MFA
When you configure the Access Portal, the Firebox generates an Access Portal certificate that you download from the Configuration Instructions page. You upload this certificate to AuthPoint when you create a SAML resource for the Access Portal.
The Access Portal certificate you download is valid for one year from the date you select the Enable SAML check box in Fireware. After you install the certificate, you can view the certificate expiry date in Fireware Web UI.
When an Access Portal certificate expires, a new certificate is generated automatically, and the Firebox generates an event log message with Message ID 7600-0000. In Fireware System Manager, you can enable notifications for events with Message ID 4001-0004 when a certificate expires. For more information, go to Enable Notifications for Specific Messages.
After the Firebox generates a new Access Portal certificate, you must upload the new certificate to your SAML resource in AuthPoint.