Applies To: AuthPoint Multi-Factor Authentication, AuthPoint Total Identity Security
If authentication does not work as expected, or if a failure occurs, you can use reports, alerts, and audit logs to troubleshoot the issue. To get started, consider all the steps in the authentication process, based on the configured resource type and access policies. Start to troubleshoot the last step of the authentication process and work back.
Here are some examples of things to check:
- Does the user receive a push notification? (if push authentication was configured)
- Is there an audit log for the authentication attempt?
- For authentication flows that require the Gateway, what information appears in the Gateway log files?
- If your policy has a policy object, do you have a second policy for the same groups and resources without the policy objects?
Steps to troubleshoot specific AuthPoint issues depend on the type of problem, and which AuthPoint and external components are involved in the authentication process. Some AuthPoint components, such as the Gateway, have local log files that you can use for troubleshooting.
For more troubleshooting information, see AuthPoint Tips and Best Practices.
Tools to Troubleshoot AuthPoint
To troubleshoot most AuthPoint issues, look at the AuthPoint reports, audit logs, and alerts.

Audit logs are often a useful starting point to troubleshoot AuthPoint issues.
To get started, look at the information available in WatchGuard Cloud and the AuthPoint Gateway log files.
AuthPoint Reports
Reports show information about AuthPoint activity and events. Some useful reports for troubleshooting include:
- Denied Push Notifications — See if the user denied a push notification
- Resource Activity — See which resources users fail to authenticate to
- Authentication — See authentication failures for each user
- Sync Activity — See the LDAP user synchronization history
For more information about reports, see Monitor AuthPoint.
Alerts
WatchGuard Cloud generates alerts for events based on notification rules. For example, you see an alert when a Gateway connects or disconnects, and when a user denies a push authentication request. You can add notification rules to generate other types of alerts.
For more information, see Manage WatchGuard Cloud Alerts.
Audit Logs
Audit logs show events related to management actions, configuration changes, and AuthPoint events. For authentication events, the Audit Log Detail window shows details about the authentication attempt.

Match the error code from the audit log in WatchGuard Cloud to the error code you see in the log messages for events on the Gateway or in authentication error messages in the IdP Portal or Logon app for Windows or Mac. For more information, see See Audit Logs.
Gateway Log Files
For authentication types that involve the AuthPoint Gateway, look at log files on the Gateway. Log messages include information about Gateway operations, and connections to RADIUS, LDAP, and ADFS. The Gateway runs as four services (Gateway, RADIUS, LDAP, and ADFS) and each service creates a separate log file. For more Gateway troubleshooting information, go to Troubleshoot the AuthPoint Gateway.
Log messages include the user name and request ID, which can be useful to match a log message to an associated AuthPoint audit log event or error message.
You can find the Gateway log files in this directory: C:\ProgramData\WatchGuard\AuthPoint\logs.
You can find the Gateway runtime log file in this directory: C:\Program Files (x86)\WatchGuard\AuthPoint Gateway\.
By default, the ProgramData folder is hidden in Windows. To open the folder, press Windows key + R, type %ProgramData%, and click OK.
Tips to Troubleshoot AuthPoint
Here are some tips to troubleshoot issues with specific types of authentication or AuthPoint components. In most cases, try to find:
- The error codes associated with the error
- The request ID associated with the error
You can then use that information to search the Audit log and log messages.
Troubleshoot the AuthPoint Gateway
The AuthPoint Gateway runs as four services: Gateway, RADIUS, LDAP, and ADFS.
| Service | Description | Port |
|---|---|---|
| WatchGuard AuthPoint Gateway | Communicates with WatchGuard Cloud and configures the other three services. | TCP port 9000 |
| WatchGuard AuthPoint RADIUS | Communicates with RADIUS clients. | TCP port 9001 |
| WatchGuard AuthPoint LDAP | Communicates with the LDAP database to authenticate LDAP users. Primary Gateways also use this service to import LDAP users to AuthPoint. | TCP port 9002 |
| WatchGuard AuthPoint ADFS | Communicates with ADFS. | TCP port 9003 |
The Gateway uses these TCP service ports for internal communication between the different Gateway services. If other applications use these TCP service ports, the Gateway might fail to start or appear offline.
To verify these ports are not in use, you can use command prompt to run the command Netstat -ano |findstr 900. This command finds anything that begins with 900.
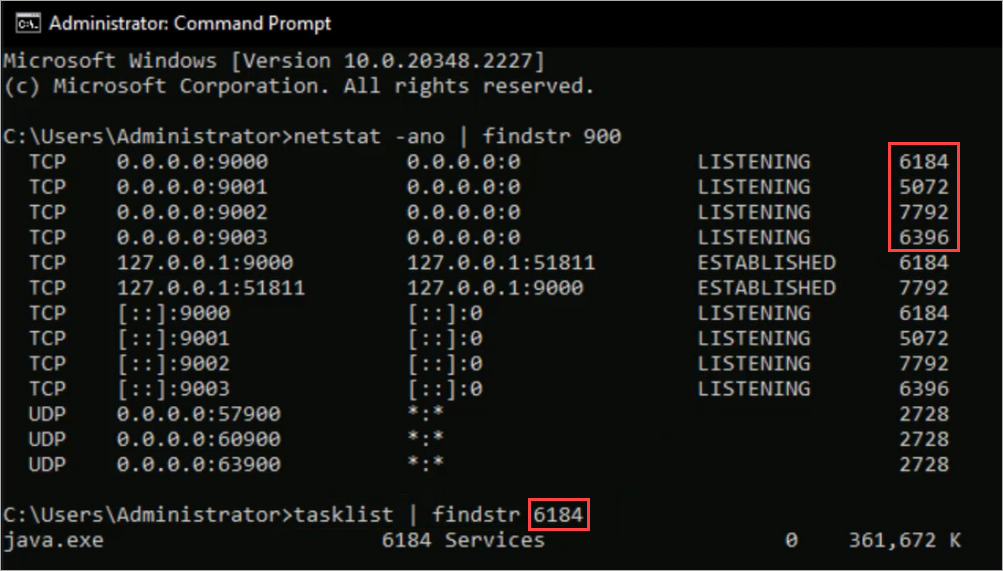
If one of the necessary ports is in use, you can run the command Tasklist | findstr process ID to identify which process is using that particular port.
When you use the tasklist command, the AuthPoint Gateway is java.exe. You can expect to see that if you already have a Gateway installed.
You can use the Windows Services app to verify that all four services are running. In the Services app, the four running services look like this:

If a service is not running, use Windows Event Viewer to see when the service stopped and started.
The Gateway service must start and run correctly before the other services will start. If the Gateway service cannot connect to the cloud, or cannot start for some reason, the other services will hang while they wait for configuration files that never arrive. If you successfully restart the Gateway service, you must also restart the other services after the Gateway service is running correctly again.
In some cases, antivirus software can cause the installation of the Gateway to fail.
If you have issues with the Gateway after installation, look at the audit logs and log files on the Gateway.
- Review the audit logs in WatchGuard Cloud and verify if any user authentications appear
- Review the runtime log file on the Gateway server at C:\Program Files (x86)\WatchGuard\AuthPoint Gateway\ to see if the Gateway has crashed.
- Review the Gateway communication log files on the Gateway server at C:\ProgramData\WatchGuard\AuthPoint\logs\ to see what is happening, in case there is a port conflict or some other issue.
- You should also verify the details for your user account, such as the group membership, AuthPoint authentication policies, and make sure your password is correct (remember that passwords are case sensitive). If you are a Service Provider, make sure the user belongs to the correct AuthPoint account.
If your issue is related to the software itself (the Gateway does not start, or something crashes or hangs), go back to the installation directory on the Gateway server and open the log folder. The installation directory is C:\Program Files (x86)\WatchGuard\AuthPoint Gateway\.
If the Gateway is not crashing, but you encounter communication issues, go to C:\ProgramData\WatchGuard\AuthPoint\logs\ and look at the Gateway log files there. In this directory, each of the different components has their own log files. There are current log files and historical log files. Historical log files are in a zip file with the date appended to the file name. If your issue is happening now, you should look at the current log file.
Troubleshoot RADIUS Authentication
Look at these log messages and error messages for useful information:
- Audit logs in WatchGuard Cloud
- RADIUS logs on the AuthPoint Gateway
- RADIUS client error messages
- Firebox log messages — If the Firebox is configured as a RADIUS client, search Firebox log messages for user authentication events, and connection errors between the Firebox and the AuthPoint Gateway.
Other things to try:
- Make sure the RADIUS port (the default ports are 1812 or 1645) is open on the server on which the Gateway is installed. The port is not open by default. If the port is open, make sure it is not used by anything else on that server, which would cause a conflict with the Gateway.
- Do a pcap between the Gateway and the RADIUS client.
If you configure Mobile VPN on a Firebox to use more than one authentication server, users who do not use the default authentication server must specify the authentication server or domain before the user name. For example, ad1_example.com\j_smith.
Troubleshoot LDAP Authentication
Look at these log messages:
- In the LDAP logs on the Gateway, look for:
- Connectivity test results
- Synchronization events
- User authentication requests
- Errors with connections to the domain controller
- In the WatchGuard Cloud audit logs, look for:
- LDAP external identity configuration changes
- LDAP user synchronization errors
Other things to try:
- If the Gateway is installed on a different server than the LDAP/AD server, do a pcap between the Gateway and the LDAP/AD server to verify that an LDAP response comes back.
Do not add the same LDAP group to multiple group syncs or create multiple group syncs that include the same LDAP user. A user synced from an LDAP database cannot belong to more than one local AuthPoint group. If an LDAP user belongs to multiple group syncs, each time AuthPoint syncs with your LDAP database, the local AuthPoint group that the user belongs to might change.
To add LDAP users to multiple groups in AuthPoint, we recommend that you enable the Create new synchronized groups toggle in your group sync and use your Active Directory group structure to manage your users.
Troubleshoot External External Identities
If the connection test to your external identity fails and NPS is running on the Gateway server, change the RADIUS port that the AuthPoint Gateway uses.
If the connection test to your external identity is successful but AuthPoint does not sync users, we recommend that you verify the credentials and permissions of the system account user. If your Active Directory instance does not use LDAPS, make sure you disable the LDAPS toggle for the external identity.
If AuthPoint successfully syncs users, but some users are not synced, make sure the missing user accounts have a valid email address that is not already used by another AuthPoint user, and that all required fields (such as first name and email address) have a value. You should also make sure that your AuthPoint license supports the number of users you want to sync. If your group sync returns more users than you have available AuthPoint licenses for, the sync only creates as many users as your license supports.
Troubleshoot AuthPoint Agents for Windows and Mac
When an authentication error occurs, an error message might appear on the AuthPoint Agent for Windows or Mac login page. The error message includes the error code and request ID. Use the error code and request ID to find the error in the WatchGuard Cloud audit logs.
When you troubleshoot the agents for Windows and Mac, look at the IP addresses involved in communication. This information can help you narrow down which audit logs to look at.
- If the user is on your local network, then the public IP of your network should appear in the WatchGuard Cloud audit logs.
- If the user uses an RDP connection to another computer on your network, then the private IP of the computer they connect from should appear in the WatchGuard Cloud audit logs.
- If the user goes home or on vacation, uses a VPN to connect to your corporate network, then RDPs to a machine on your network, the virtual IP address on their computer for that mobile VPN should appear in the WatchGuard Cloud audit logs.
You can also look at the configuration files downloaded by the Logon app from WatchGuard Cloud. If these files do not get updated when you make changes in AuthPoint, there is likely a communication problem. If this happens, verify that the communication between the Logon app and WatchGuard Cloud is allowed through your security software and upstream network devices.
You can see the Logon app configuration files here:
- Agent for Windows
- Configuration File: %WINDIR%\wlconfig.cfg
- Offline Policy Cache: %WINDIR%\drivers\etc\wlconfig.cfg
- Agent for macOS
- Configuration File: /Library/Application Support/WatchGuard/wlconfig.cfg
- Log File: /Library/Logs/WatchGuard/AuthPoint Agent/
If you run into issues installing the AuthPoint agent for Windows:
- You can use various logging switches, such as msiexec <filename> /l*v to gather more information. In addition to the log messages related to these commands, you can also look at the Windows event logs for more information.
- Verify the permissions of the user account that you use to install the agent.
- (Service Providers) If you have multiple AuthPoint accounts, make sure that you use the configuration file from the correct account.
Troubleshoot IdP Portal
To troubleshoot the IdP portal, ask the user for information about login errors. When authentication fails, an error message appears on the login page. The bottom of the page shows the error code and request ID.
Use the error code and request ID to find the error in the audit log.
Troubleshoot AuthPoint Mobile App
To troubleshoot the mobile app, ask the user for information about login errors. When an authentication error occurs, the mobile device shows an error message that includes the error code. Errors are useful for troubleshooting, because you can look for the error code in the audit log.
In the mobile app, the user can also see token details. Make sure that the token details show these values:
- Push Status — Registered
- Time Reference — The correct time
If needed, the user can select the Sync Token option to resynchronize the time and status of a token with the server. This is necessary for authentication so that when the user approves a push or type an OTP, AuthPoint recognizes that the authentication happens in the allowed amount of time. If the time difference between the token timestamp and the server timestamp is too big, the user may not be able to authenticate.
For more information, see Sync Your Token.
If a user has trouble with push notifications, you can try these troubleshooting options:
- Use the User Verification feature to test whether the user receives a push notification.
- Have an operator view the token details for the user to make sure that push notifications are allowed on the user's device. The user can also verify this in the mobile app under Device Information. If either test shows that push is not allowed, the user must allow notifications for the AuthPoint app.
For Android devices, we recommend that you set the notification style to Detailed.
- Ask the user to turn off battery optimization or turn on auto-start for the AuthPoint app. Often, battery optimization or app settings can cause push notification issues. On some devices, battery optimization features prevent auto-start for apps.
- Have the user make sure they have a reliable Internet connection.
- We also recommend that you configure the mobile settings listed below for the AuthPoint mobile app:
- Allow notifications on the lock screen
- Allow background and roaming data
- Allow the app while data saving is on
- Allow background activity
- Allow autostart
- Turn off battery saver
Troubleshoot ADFS
To troubleshoot ADFS, you can find useful information in:
- Event viewer on the computer where the ADFS Agent is installed
- Audit logs in WatchGuard Cloud
- ADFS log file on the AuthPoint Gateway
- ADFS agent log file
Troubleshoot RD Web
The AuthPoint Agent for RD Web runs as a service on the RD Web server. Make sure the WatchGuard AuthPoint RD Web Core service is running.
Tools you can use to troubleshoot RD Web include:
- IIS server log files — For information about user authentication to the RD Web portal
- Event Viewer for Remote Desktop Services — For information about user connections to RD Web hosted resources
- AuthPoint audit logs — For events for RD Web user authentication